Functions of the Skeleton:
The skeleton supports the body, protects internal organs from dangers in the external environment, provides for movement, stores important minerals, and provides structure, so you aren't just a sack of blood and organs.
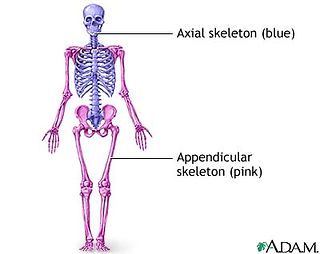
Axial vs. Appendicular Skeletons:
The axial skeleton is composed of three parts: the ribcage, the skull, and vertebrae.
The appendicular skeleton is composed of all the other bones.
What are the types of bone cells?:
Osteoclasts are a type of bone cell that breaks down bone in order to release minerals in a process called bone resorption.
Osteoblasts are bone cells that produce and build more bone.
How are bones formed?:
A fetus' cartilage body turns into bone through the process of ossification, which is how bones are made by adding minerals around bone cells so that it hardens from cartilage into bone. Cartilage is a kind of connective tissue that is similar to bone because it supports and structures the body but it is softer and more malleable than bone.
Joint: space where bones meet

